Chronic pain is a debilitating condition that affects millions of people worldwide. According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), approximately 20% of adults in the United States suffer from chronic pain, and this number is increasing. Chronic pain can have a significant impact on a person’s quality of life, leading to depression, anxiety, and social isolation.
What is Chronic Pain?
Chronic pain is defined as pain that lasts for 3 months or longer. It can be caused by a variety of factors, including injury, illness, or nerve damage. Chronic pain can also develop without any apparent cause. It can affect any part of the body and can range from mild to severe.

Types of Chronic Pain

There are several types of chronic pain, each with its own set of symptoms and causes. The most common types of chronic pain include:
- Back Pain: This type of chronic pain affects the lower back and can be caused by a variety of factors, including injury, muscle strain, or nerve damage.
- Headaches: Chronic headaches are a common type of chronic pain and can be caused by tension, sinus problems, or migraines.
- Neuropathic Pain: This type of chronic pain is caused by nerve damage and can be experienced as a burning, tingling, or shooting sensation.
- Arthritis Pain: Arthritis pain is caused by inflammation in the joints and can result in stiffness, swelling, and decreased range of motion.
- Fibromyalgia: Fibromyalgia is a chronic pain condition that affects the muscles and soft tissues, causing widespread pain and tenderness.
Causes of Chronic Pain

Chronic pain can be caused by a variety of factors, including:
- Injury: Chronic pain can develop as a result of an injury, such as a broken bone or a sprain.
- Medical Conditions: Chronic pain can be a symptom of many medical conditions, including arthritis, fibromyalgia, and neuropathy.
- Nerve Damage: Nerve damage can result in chronic pain, such as in the case of neuropathic pain.
- Surgery: Chronic pain can develop after surgery, particularly in cases where nerves have been damaged.
- Lifestyle Factors: Lifestyle factors such as poor posture, lack of exercise, and stress can contribute to chronic pain.
Treatment of Chronic Pain
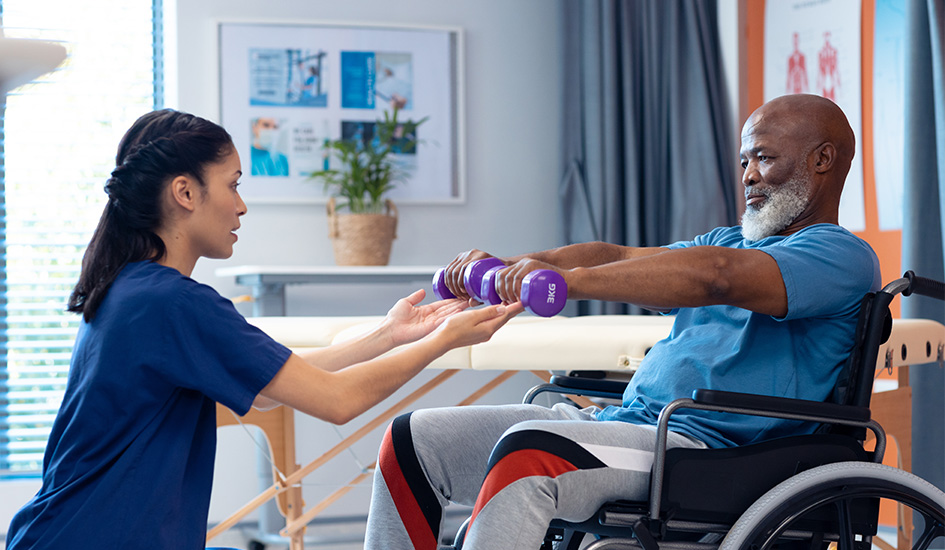

There is no single treatment for chronic pain, and treatment options can vary depending on the cause and severity of the pain. However, there are several treatment options available that can help manage chronic pain, including:
- Medications: Medications such as nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), opioids, and antidepressants can be used to manage chronic pain.
- Physical Therapy: Physical therapy can help manage chronic pain by improving mobility, strength, and flexibility.
- Mind-Body Techniques: Mind-body techniques such as meditation, deep breathing, and yoga can help manage chronic pain by reducing stress and promoting relaxation.
- Alternative Therapies: Alternative therapies such as acupuncture, massage, and chiropractic care can be used to manage chronic pain.
- Surgery: In some cases, surgery may be necessary to treat chronic pain, particularly in cases where nerves have been damaged.
Living with Chronic Pain
Living with chronic pain can be challenging, and it is important for people with chronic pain to take steps to manage their pain and improve their quality of life. Some tips for living with chronic pain include:
- Establishing a Support System: It is important for people with chronic pain to have a support system of friends, family, and healthcare professionals who can provide emotional and physical support.
- Practicing Self-Care: Practicing self-care activities such as taking breaks, getting enough sleep, and engaging in relaxing activities can help manage chronic pain